Thumb Arthritis
The Ache in Every Grip
by Amanda E. Lampong
Thumb Arthritis, which affects the base of your thumb, is often referred to as basal joint arthritis or carpometacarpal (CMC) joint arthritis. This condition can make daily tasks become challenging due to the pain, stiffness, and decreased thumb motion. It is a common aging condition that develops as the cartilage on the ends of the bones that make up the joint at the base of your thumb wears away. It can also result from prior trauma or injury to the thumb joint.
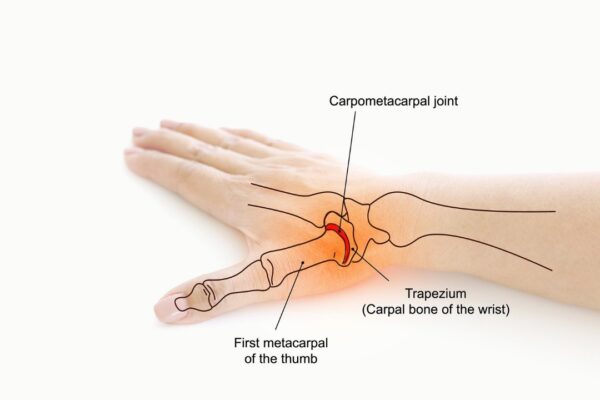
Normal thumb joints have cartilage covering the ends of the bones, which serves as a cushion and permits the bones to move easily against one another. The smooth surface of the cartilage that covers the tips of the bones in the thumb becomes more uneven due to arthritis. This causes friction and joint injury when the bones scrape against one another. When a joint is damaged, bone spurs, which grow along the sides of the existing bone, might develop. These lumps can be seen on the thumb joint.
The primary and most typical symptom of thumb arthritis is pain. When you hold, squeeze, or pinch anything or exert effort with your thumb, pain may develop near the base of your thumb. Other indications and symptoms could be, swelling and discomfort at the thumb’s base, a sore thumb following continuous use, weakness when using your thumb to grab or pinch, and reduction in range of motion.
Women are more likely than men to get arthritis in the base of the thumb, and it often develops after the age of 40. In addition, there may be other variables that contribute to thumb arthritis, namely:
- Obesity.
- Certain inherited disorders, such as loose joint ligament laxity and malformed joints.
- Fractures and sprains that affect the thumb joint.
- Professions and activities that place a lot of strain on the thumb joint.
Thumb arthritis develops as a result of cartilage tissue deterioration. This condition is typically treated with a combination of medication and surgery. However, surgery may take time to heal and rehabilitate.
At Swiss Stem Cell, stem cell therapy is a non-surgical method that can be considered. It is an option for therapy that is highly effective to avoid thumb surgery. The Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) are used to release proteins known as cytokines that reduce the cartilage degeneration. When the injured area is treated with stem cells, the thumb ligament is repaired and healthy tissue is generated. In addition, stem cells maintain the health of the cartilage around the joint, preventing further damage.
Even though conventional treatment methods for thumb arthritis would provide pain relief, they might not cure the underlying problem. Stem cells are the unique cells with the potential to restore tissue. Therefore, stem cell therapy can treat illness non-surgically and at the same time promotes tissue regeneration.
If you have any thumb pain or injury, stem cell therapy can be an option for tissue healing and pain relief. Contact Swiss Stem Cell today to schedule your consultation.
